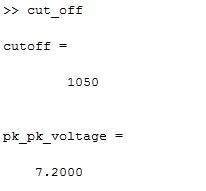Week
10: 3/21/2016 – 3/25/2016
Blogsheet
week 10
In
this week’s lab, you will collect more data on low pass and high pass filters
and process them using MATLAB.
PART
A: MATLAB practice.
1.
Open MATLAB. Open the editor and
copy paste the following code. Name your code as FirstCode.m Save the resulting
plot as a JPEG image and put it here.
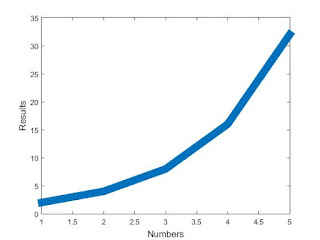
Our results are plotted below as graph 1.
clear
all;
close
all;
x
= [1 2 3 4 5];
y
= 2.^x;
plot(x,
y, 'LineWidth', 6)
xlabel('Numbers',
'FontSize', 12)
ylabel('Results',
'FontSize', 12)
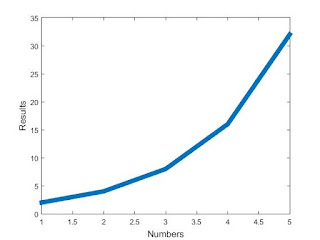 |
| Graph 1: This is the plot to the code above. |
2.
What does clear all do?
Clear all removes all variables from the current work space
3.
What does close all do?
Close all closes all figures in the current work space
4.
In the command line, type x and
press enter. This is a matrix. How many rows and columns are there in the
matrix?
There are 5 columns and 1 row in the matrix. A picture is below.
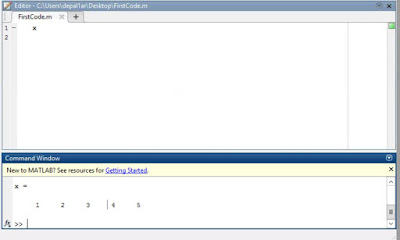 |
| Picture 1: This is a picture of what happens when you run X in the command line. |
5.
Why is there a semicolon at the end
of the line of x and y?
There is a semicolon to suppress the command. It prevents MATLAB from plotting the matrix x = [1 2 3 4 5]
6.
Remove the dot on the y = 2.^x; line
and execute the code again. What does the error message mean?
We got the error in the picture below. If you remove the dot X is not a matrix anymore and due to setting X as a matrix previously in the code it causes an error.
 |
| Picture 2: This is a picture of the error described in question 6. |
7.
How does the LineWidth affect the
plot? Explain.
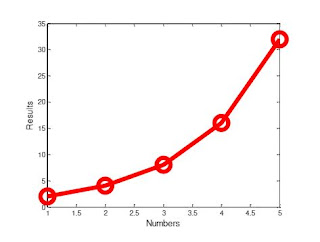
The LineWidth changes how thick the plot is. Below is a picture of the same code from #1 but with 'LineWidth', 10.
 |
| Graph 2: This graph is identical to the one in question one, except that the line is thicker. |
8.
Type help plot on the command line
and study the options for plot command. Provide how you would change the line
for plot command to obtain the following figure (Hint: Like LineWidth, there is
another property called MarkerSize)
 |
| Graph 3: This is the graph we are supposed to replicate for question 8. |
To change the code we adjusted the Linewidth, included MarkerSize, and MarkerEdgeColor. A picture of our code is below.
 |
| Picture 2: This is our code to make the graph for question 8. |
9.
What happens if you change the line
for x to x = [1; 2; 3; 4; 5];? Explain.
It creates multiple rows for the matrix. Instead of having 1 row with 5 columns it will have 5 rows with 1 column.
11. Degree vs. radian in MATLAB:
a.
Calculate sinus of 30 degrees using
a calculator or internet.
sin(30 degrees) = .5
b.
Type sin(30) in the command line of
the MATLAB. Why is this number different? (Hint: MATLAB treats angles as
radians).
In MATLAB sin(30) = -0.9880. This number is different because it is the value calculated with 30 radians, not degrees.
c.
How can you modify sin(30) so we get
the correct number?
You can change the number from radians to degrees. If you multiply 30 by pi/180 you can get sin(.5235987756) which is equal to .5. Another way to get the correct number is modify sin(30) into sind(30).
12. Plot y = 10 sin (100 t) using Matlab
with two different resolutions on the same plot: 10 points per period and 1000
points per period. The plot needs to show only two periods. Commands you might
need to use are linspace, plot, hold on, legend, xlabel, and ylabel. Provide
your code and resulting figure. The output figure should look like the following:
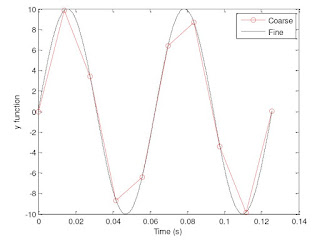 |
| Graph 4: This is the graph we are supposed to replicate for question 12. |
Our output and code are below:
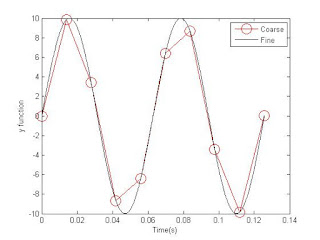 |
| Graph 5: This graph is our result in trying to replicate Graph 4. |
 |
| Picture 3: This picture is our code for graph 5. |
13.
Explain what is changed in the
following plot comparing to the previous one.
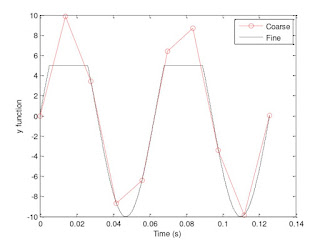 |
| Graph 6: This graph is given and has a cutoff point for the fine line at 5. |
The range on the fine function in this plot has been limited to (-10,5). In the plot in number 12 the range of both functions was (-10,10).
14.
The command find was used to create
this code. Study the use of find (help find) and try to replicate the plot
above. Provide your code.
Using the find function we were able to create code that replicated this graph. Below is our output and a picture of our code.
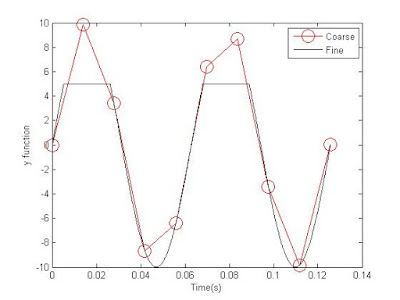 |
| Graph 7: This is our replication of graph 6. |
 |
| Picture 4: This is our code for graph 7. |
PART
B: Filters and MATLAB
1.
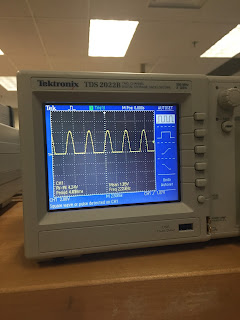
Build a low pass filter using a
resistor and capacitor in which the cut off frequency is 1 kHz. Observe the
output signal using the oscilloscope. Collect several data points particularly
around the cut off frequency. Provide your data in a table.
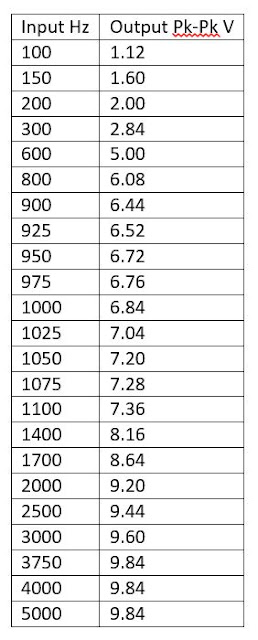
We built the low pass filter, the table below contains our input and output measurements. We used 5 V as our input and read peak to peak voltage.
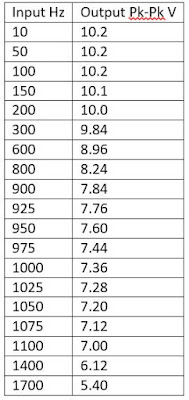 |
| Table 1: This is our data for the low pass filter. Our input voltage is 5V and our output is read in pk-pk voltage. |
2.
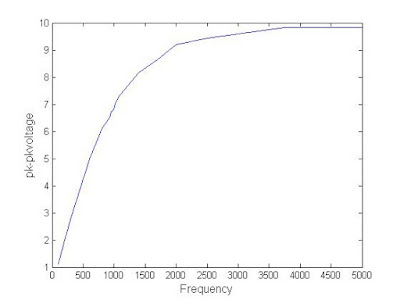
Plot your data using MATLAB. Make
sure to use proper labels for the plot and make your plot line and fonts
readable. Provide your code and the plot.
 |
| Graph 8: This graph is our data from above plotted to show a low pass filter. |
 |
| Picture 5: This is our code for the graph above. |
3.
Calculate the cut off frequency
using MATLAB. Find command will be used. Provide your code.
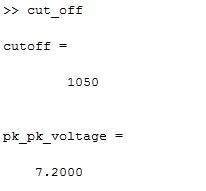 |
| Picture 6: This is our calculated cut off value from MATLAB. |
 |
| Picture 7: This is the code to calculate our value. |
4.
Repeat 1-3 by modifying the circuit
to a high pass filter.
A.
 |
| Table 2: This is our table for the high pass filter. |
B.
 |
| Graph 9: This graph is our data for a high pass filter plotted. |
 |
| Picture 8: This is our code for the graph above. |
C.
Picture 9: This is the calculated cutoff value fromMATLAB.
 |
| Picture 10: This is our code for the MATLAB calculation above. |